Top
Demography Special Lecture I, II
Latest update: 1 August 2015 (Sat) | 2014 | current year
1. Overview
Demography is one of the essential methodology to grasp the characteristics of human population survival. It can support the understanding of epidemiology and public health. This lecture basically use a textbook for basic formal demography and demographic models, followed by several examples of actual demographic researches.
Using computer practices may be helpful for understanding. Bringing your own laptop computer is recommended. Software to be used is GNU R, which is free software (http://www.r-project.org).
2. Plan
The lecture is done in first semester on Thursday, 13:00-14:30 at GSICS 206.
- Introduction (9 April 2015, handout)
- Data collection: Basically 3 ways (Census, Vital Registration and Sample Survey). (16 April 2015, handout)
- Age and sex structure (23 April 2015, handout and R code).
- Period fertility (30 April 2015, handout; R code; Tables in Excel format: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7; Tables in tab-delimited text format: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7; Exercises data: 4E.1, 4E.2, 4E.3, 4E.4; Data in Excel format: Tables 4E.1-4E.4, Table 5.1-5.5)
Appendix: asfrworld.R
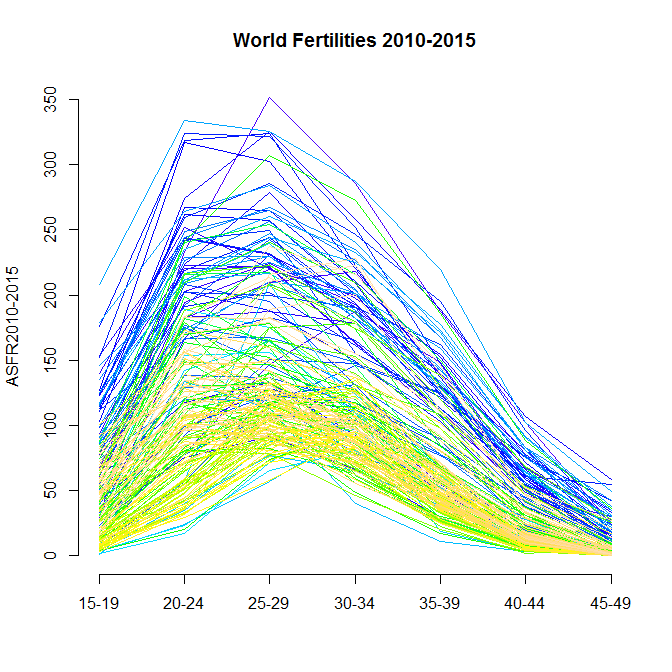
(animation with Japan enhanced is made by this code)
- Cohort fertility (7 May 2015, handout; R code; Tables in tab-delimited text: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6; Table 5.6 Excel Worksheet), (Exercises: Excel format data, Tables in tab-delimited text: 5E-1, 5E-2, 5E-3, 5E-4, 5E-5; R code to answer the exercises of Chapter 5)
- Mortality and life tables (14 May 2015, handout; R code for CDR, IMR, etc.; R code for lifetable; Supplementary explanation; Excel worksheets are also available as tables-6.xls; Additional explanation) The data and answers to Exercises: Excel file, R code and comments.
- Migration (21 May 2015, handout, R code to see the relationship between gross migration and net migration in Japan 2013, R code to compare the population pyramids among all prefectures, R code to see the relationship between PEI [population expanding index] and YP [youth population] by prefecture.)
- Marriage and divorce (28 May 2015, handout, R code for text and R code for exercises.)
- Reproducibility (4 June 2015, handout, R code for text, R code with comments for exercise, R code to calculate TFR, GRR and NRR for Japan 2010.)
- Models of age structure (11 June 2015, handout, R code for text, R code for exercises.)
- Model life tables (18 June 2015, handout, R code for Chapter 12 and its exercises, R code for Chapter 13)
- Models of nupitiality and fertility (25 June 2015, handout, R code, cf. Bongaarts' proximate determinants model: Johns Hopkins, IUSSP's e-learning material)
- Population projections and forecasts (2 July 2015, handout, R code, "Lesson 8: The Cohost Component Population Projection Method" at M & E Learning Center, Cohort-component population projections at IUSSP'e-learning)
- International migration and examples of demographic analysis in Senegal or other countries (lecture given by Dr. Reiko Hayashi, on 9 July 2015)
- Microsimulation models (16 July 2015, handout, simulation conditions setting R code called by other code, calculate initial population and save R code, execute simulation R code)
3. Evaluation
Based on presentation, discussion, and report (subject will be given on 9 July).
4. Textbook
Newell C (1988) Methods and models in demography. The Guilford Press
(Reference) Preston SH, Heuveline P, Guillot M (2001) Demography: Measuring and Modeling Population Processes. Blackwell Publishing.
5. Office hour
For the students of the Graduate School of Health Sciences, Tuesday, 18:00-18:30, at Myodani campus E707. For the students of GSICS, Thusday, 16:40-18:00 at Frontier Building Room 717. Taking appointment is recommended.
6. Message to the students
Done in English.
Notice to cite or link here | [TOP PAGE]

